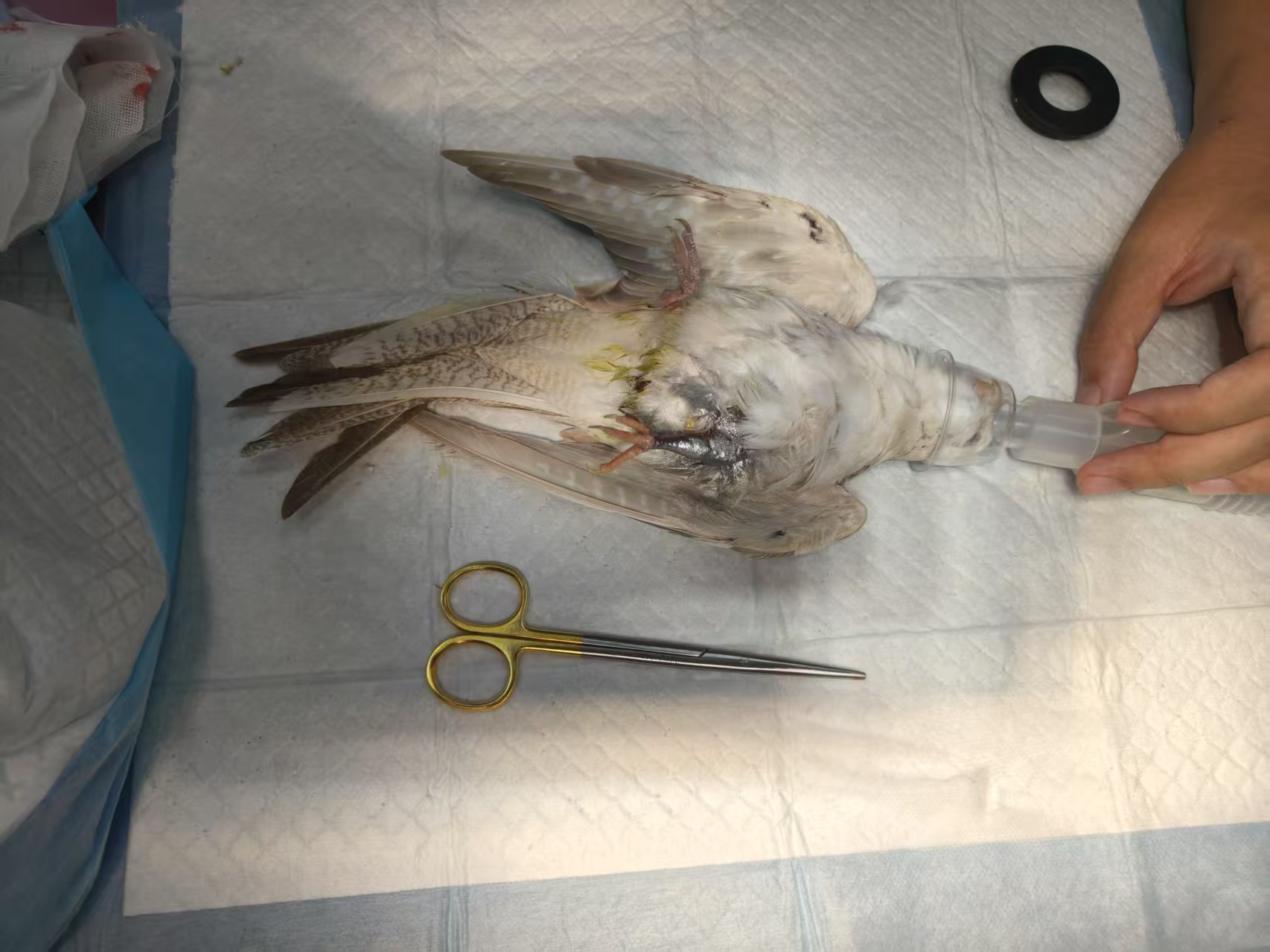
As exotic animal medicine continues to evolve, end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO₂) monitoring is becoming an essential tool in the clinical management of non-traditional pets. Whether during anesthesia, sedation, recovery, or emergency care, ETCO₂ provides real-time, non-invasive, and dynamic assessment of ventilation status, significantly enhancing clinical safety and control.
ETCO₂ reflects the partial pressure of carbon dioxide at the end of exhalation, serving as an important physiological indicator of alveolar ventilation. For exotic pets—whose species diversity and physiological variability pose challenges to standardized monitoring—ETCO₂ offers a broad, adaptable, and intuitive method applicable across multiple clinical settings:
Exotic animals are highly sensitive to anesthetic agents and prone to hypoventilation. ETCO₂ monitoring enables real-time observation of changes in carbon dioxide elimination, helping veterinarians adjust drug dosing and ventilatory support as needed.
A sustained rise in ETCO₂ values or a flattening of the waveform may indicate reduced respiratory effort or airway compromise, prompting timely intervention before carbon dioxide retention leads to complications.
In procedures requiring only light sedation—such as imaging, dental care, or ophthalmic exams—exotic pets often do not undergo endotracheal intubation. In these cases, ETCO₂ serves as a valuable tool to detect early signs of respiratory depression, apnea, or reduced tidal volume that may not be visually apparent.
Attenuation or interruption of the capnogram waveform during a sedated procedure can alert clinicians to decreased respiratory drive, guiding adjustments to sedation depth or respiratory support.
During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), ETCO₂ is considered an indirect indicator of the effectiveness of chest compressions and the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). For small exotic mammals where other monitoring options may be limited, ETCO₂ is especially useful.
A sudden increase in ETCO₂ during ongoing chest compressions may suggest effective circulation or an early sign of ROSC, guiding clinical decisions during resuscitative efforts.
The recovery phase in exotic patients is often marked by irregular breathing or delayed return of normal respiratory patterns. ETCO₂ provides immediate feedback on respiratory effort and gas exchange, enabling early detection of ventilation compromise or residual anesthetic effects.
A rapid change in ETCO₂ values or waveform abnormalities during recovery may signal the need for further evaluation of airway patency, temperature, or residual sedation.
To ensure accurate and clinically meaningful ETCO₂ monitoring in exotic pets, the following points are recommended:
Select compact, species-adaptable sampling interfaces, compatible with various facial structures and respiratory modalities;
Maintain airway patency, avoiding artifacts caused by positional obstruction, secretions, or soft tissue collapse;
Minimize sampling line dead space and ensure stable connection to reduce signal delay or waveform distortion;
Use appropriate alarm thresholds (e.g., low ETCO₂, prolonged apnea) to enable early intervention;
Integrate with other parameters such as SpO₂ and temperature for a comprehensive respiratory-metabolic assessment;
Calibrate and check equipment before use, ensuring sampling lines are clean and interfaces properly fitted.
As exotic animal practice continues to advance, ETCO₂ monitoring offers a safe, real-time, and non-invasive method for respiratory assessment, increasingly recognized across a wide range of clinical scenarios. From intraoperative monitoring to recovery and emergency care, its role is expanding as an essential component of modern exotic pet management.
With proper setup, clinical integration, and patient-specific adjustments, ETCO₂ can significantly improve the quality and precision of respiratory care in exotic animals—contributing to safer outcomes and higher standards in veterinary medicine.