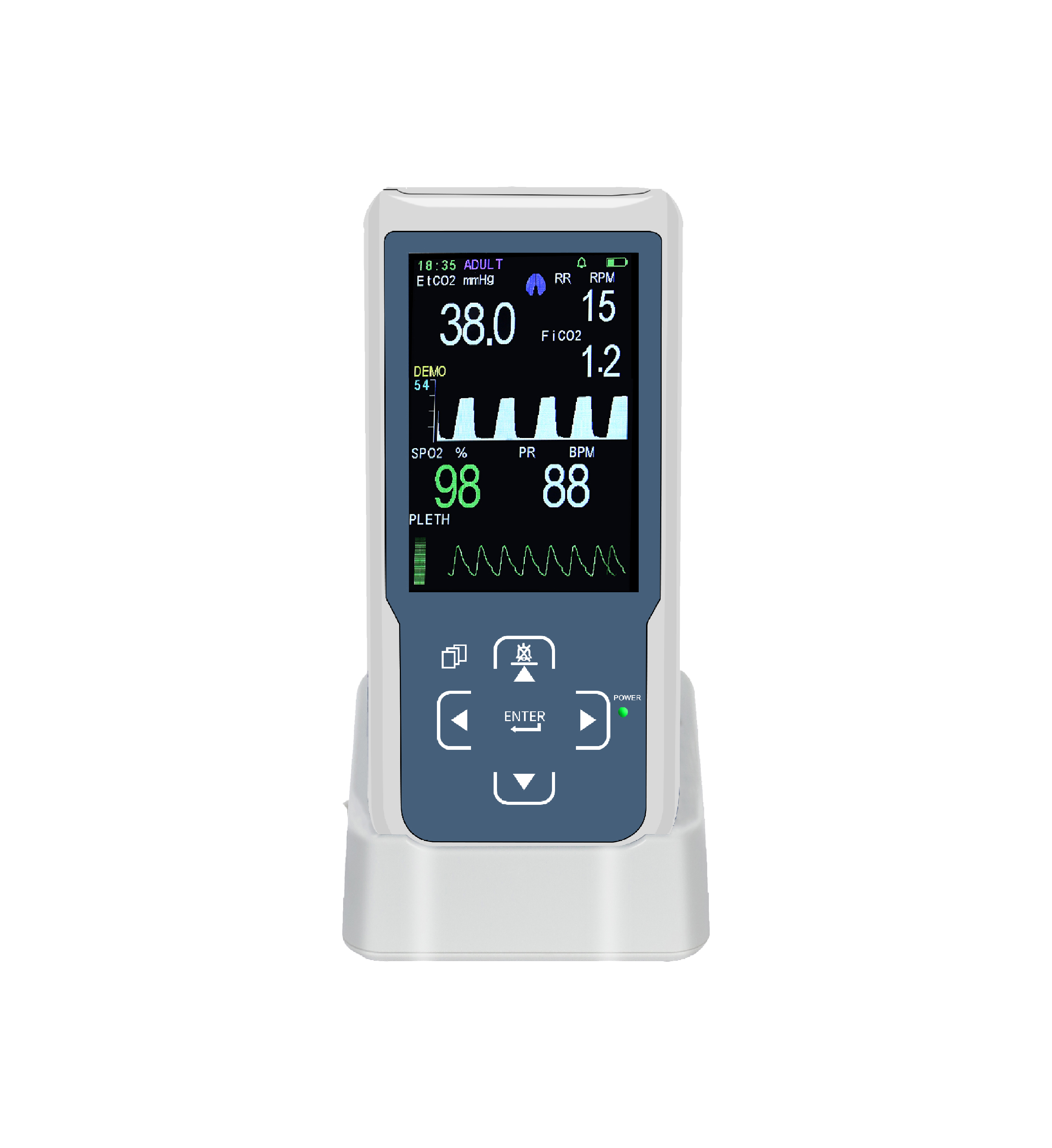






The EtCO2 Monitor measures the partial pressure or concentration of carbon dioxide in the patient's exhaled breath to assist in judging the patient's ventilation status, spontaneous breathing and circulation recovery, etc.,
And the products produced by Kingst are portable and can be used in various emergency situations. For example, first aid or pre-hospital first aid, as well as transportation inside and outside the hospital, provide convenience for medical staff and greatly improve the medical level.
The capnography waveform can directly reflect the patient's ventilation status and dead space at this time. The waveform diagram is divided into four quadrants, namely the inspiratory phase, ascending phase, alveolar plateau phase, and descending phase. The end of the alveolar plateau is the peak of ETCO2, which is also the point we monitor.
The first phase: no gas participates in the interaction, 0 baseline
The second phase: the initial, rapid rise stage of exhalation
The third phase: slowly ascending, reaching the alveolar platform
The fourth phase: rapid descent to the beginning of inspiration.
From the waveform, we can judge the patient's ventilation and dead space, so as to provide clinical guidance.
End tidal CO2 monitoring devices are used to measure the concentration of carbon dioxide in a patient's breath. A low end-tidal CO2 reading can indicate a decrease in alveolar ventilation or reduced CO2 entering the alveoli. This can be caused by mechanical ventilation with excessive tidal volume, shock, hypothermia, or artificial ventilation with a slow frequency and too large tidal volume. Tachypnea, a short peak phase, and low ETCO2 value may also occur with artificial ventilation where the frequency and tidal volume are too high. In clinical settings, low end tidal co2 meaning can indicate a problem with respiratory function, and healthcare professionals rely on EtCO2 monitoring to help diagnose and optimize treatment plans for their patients.
EtCO2 monitoring devices, or EtCO2 monitors, offer a non-invasive and real-time functional detection index for assessing lung function. This technology is a significant advancement in non-invasive monitoring, providing a clear indicator for respiratory support and management in numerous healthcare settings, including anesthesia patients, emergency departments, ICUs, and respiratory departments. EtCO2 monitoring is essential and commonly recognized as the sixth basic vital sign alongside ECG, blood oxygen, blood pressure, body temperature, and respiration. Healthcare professionals rely on EtCO2 monitors to help optimize patient care and ensure effective respiratory function.

Capnography monitor can be applied to emergency department, respiratory department, anesthesiology department, ICU, etc.
The purposes of our monitoring are: monitoring ventilation function; adjusting ventilator parameters and guiding ventilator evacuation; determining the position of tracheal tube; understanding alveolar dead space and changes in pulmonary blood flow; evaluating circulatory function during CPR; airway positioning, etc.

It is a monitor that can measure the carbon dioxide concentration or partial pressure in the patient's exhaled breath

The main purpose of monitoring ETCO2 is to judge the patient's ventilation, spontaneous circulation recovery, and the position of tracheal intubation according to the measured data, so as to provide convenient and effective help for doctors by using our portable end tidal co2 monitor.

The high or low value of portable end tidal co2 monitor may mean that the patient's ventilation has changed, it may be due to excessive ventilation or insufficient ventilation, or the working parameters of the ventilator may be set incorrectly.
