Two Different ETCO₂ Monitoring Methods: Mainstream and Sidestream
ETCO₂ (End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide) monitoring is an essential tool that provides real-time information about pulmonary ventilation efficiency. By measuring the carbon dioxide concentration in exhaled gas, it offers clinicians immediate insight into a patient’s respiratory status. Compared with traditional pulse oximetry, ETCO₂ monitoring can detect respiratory abnormalities earlier. It is widely used in anesthesia, surgery, ICU, and emergency settings.
Definition: ETCO₂ is the highest CO₂ concentration in exhaled gas at the end of expiration.
Physiological Significance:
Reflects alveolar ventilation: ETCO₂ directly indicates alveolar ventilation efficiency. Low ETCO₂ suggests hypoventilation, while rapid ventilation can also lower ETCO₂ values.
Indirectly reflects blood CO₂ levels: ETCO₂ is usually slightly lower than arterial CO₂ (PaCO₂), and continuous monitoring provides trends in blood CO₂ levels.
Early detection of respiratory abnormalities: ETCO₂ can indicate hypoventilation, hyperventilation, apnea, or airway obstruction, serving as an early warning, especially in anesthesia and critical care.
Clinical reference: ETCO₂ waveforms show the completeness of the respiratory cycle, and the changes at the end of exhalation and inhalation help clinicians evaluate airway patency and breathing patterns.
ETCO₂ monitoring primarily uses Mainstream and Sidestream methods. The principles, installation, and operational characteristics differ between the two.
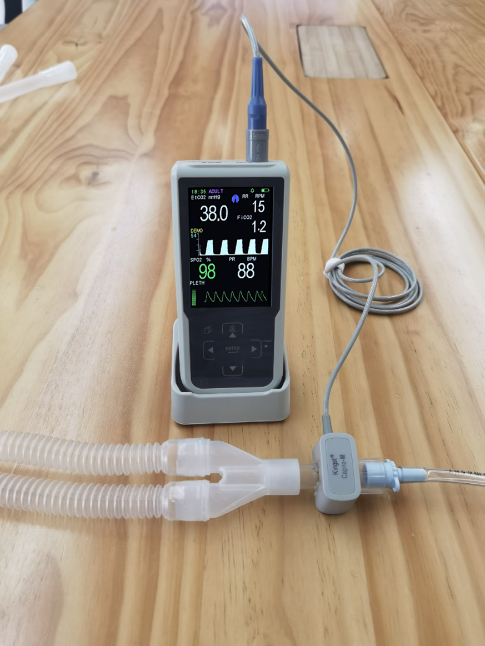
Principle: A sensor is directly installed in the breathing circuit. As gas flows through, the optical or infrared sensor measures CO₂ concentration directly, providing real-time waveforms and values.
Advantages:
High real-time response, no waveform delay
High measurement accuracy
Less affected by environmental factors such as humidity and temperature
Disadvantages:
Adds slight weight to the breathing circuit
Requires secure connection to the circuit to ensure accuracy
Operational Notes:
Calibration (zeroing) is required when replacing the breathing circuit adapter
Diagram:
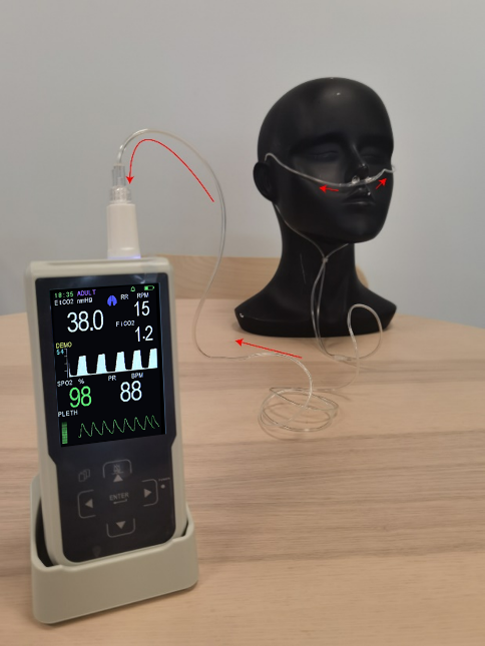
Principle: A small internal pump in the monitor draws a sample of gas from the patient’s airway through a thin tubing into the instrument, where CO₂ concentration is measured and waveforms and values are displayed.
Advantages:
Adjustable sampling flow ensures stable gas measurement
Lightweight and easy to install, with minimal added resistance to the breathing circuit
Does not add weight directly to the breathing circuit, suitable for mobile or space-limited applications
Disadvantages:
Slight waveform delay may occur
Measurement can be affected by circuit dead space; insufficient sample gas can lead to lower values
Usage Requirements:
Requires tubing connection between the patient’s airway and the monitor
Operational Notes:
Regularly replace the filter to prevent blockage that could affect measurement accuracy
Diagram: